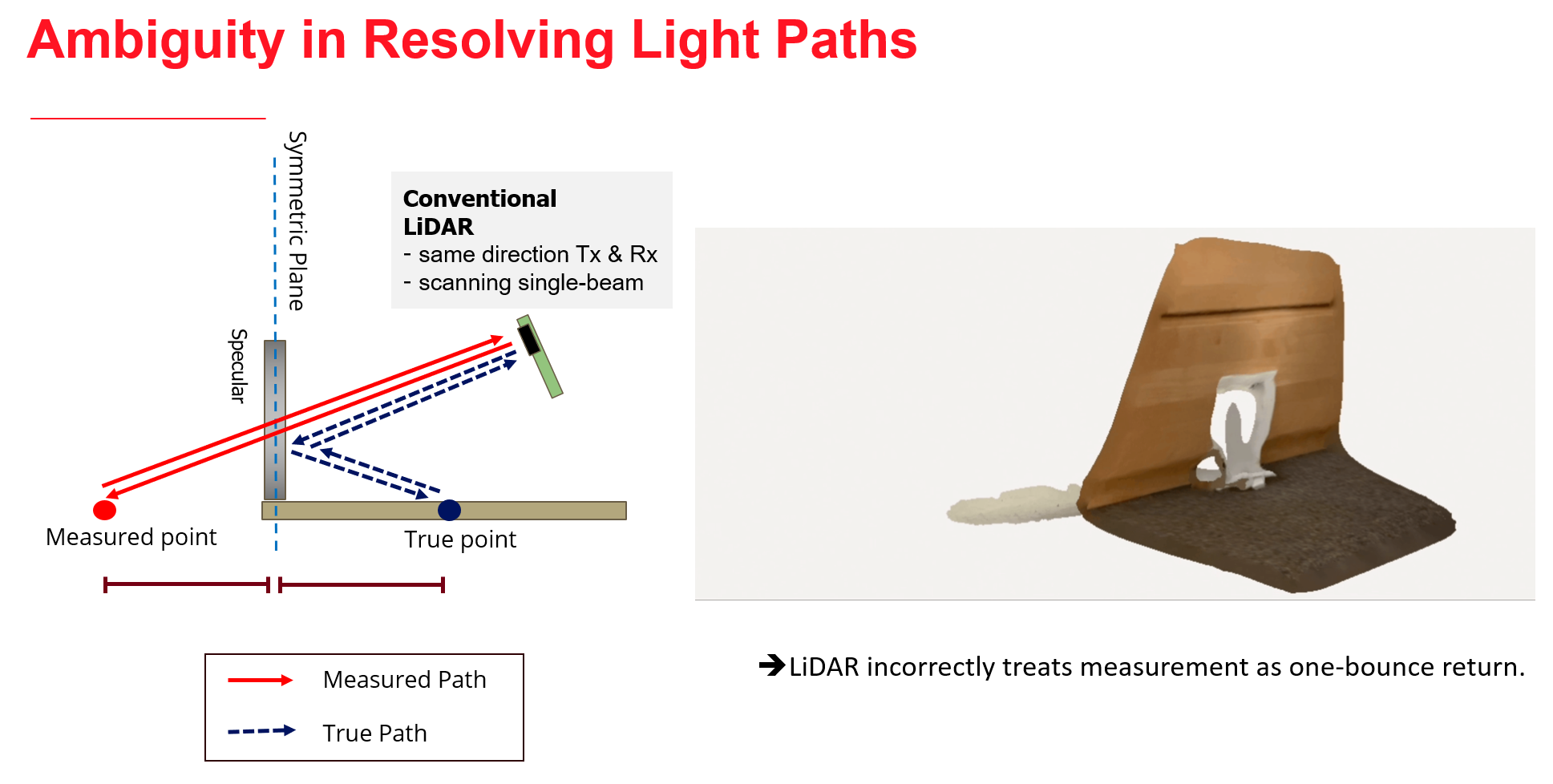
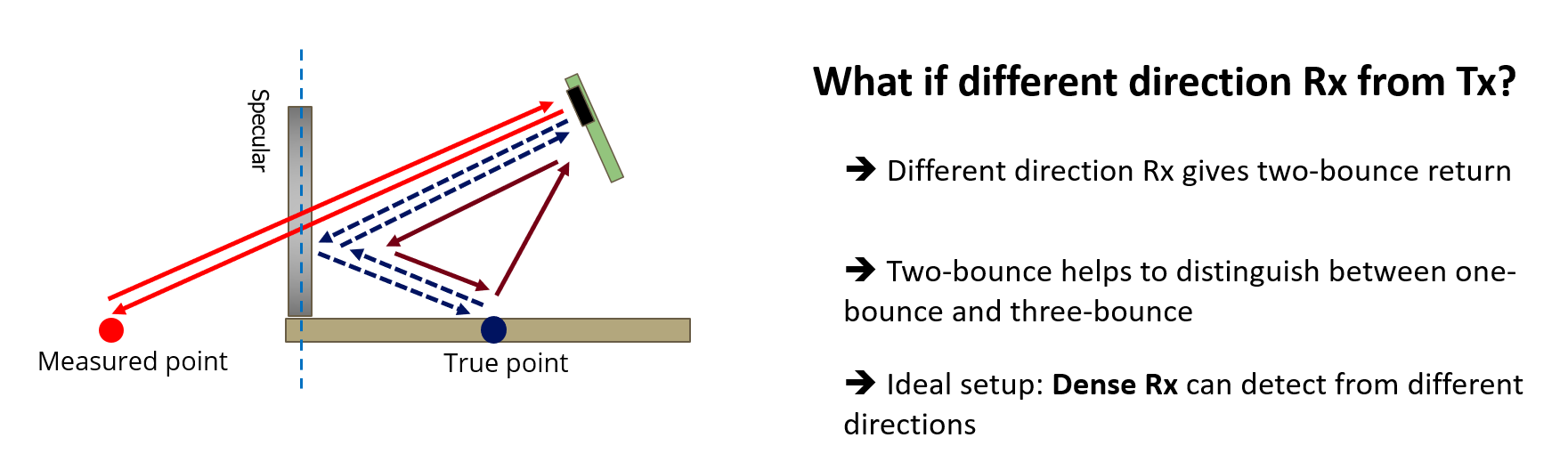
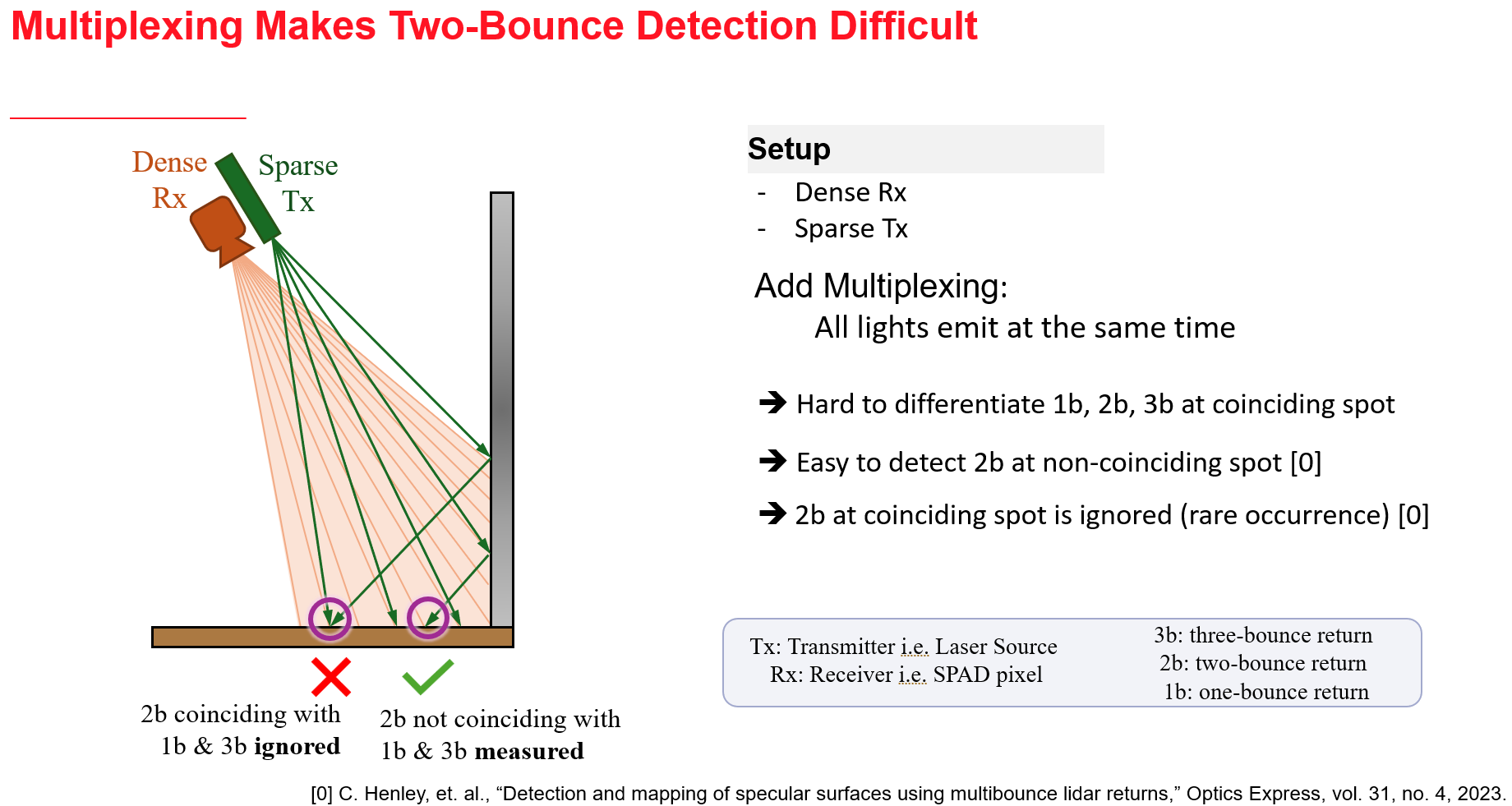
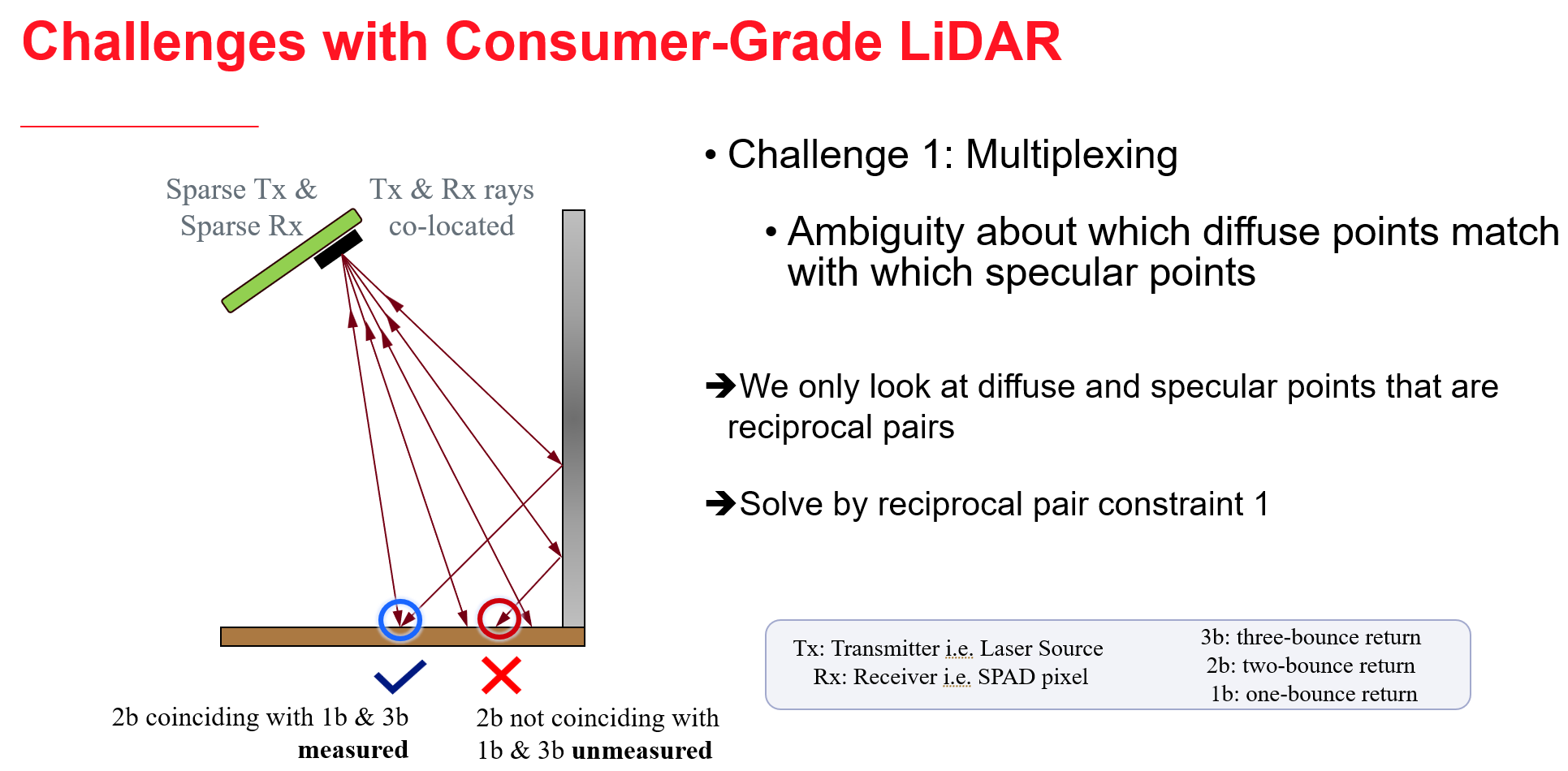
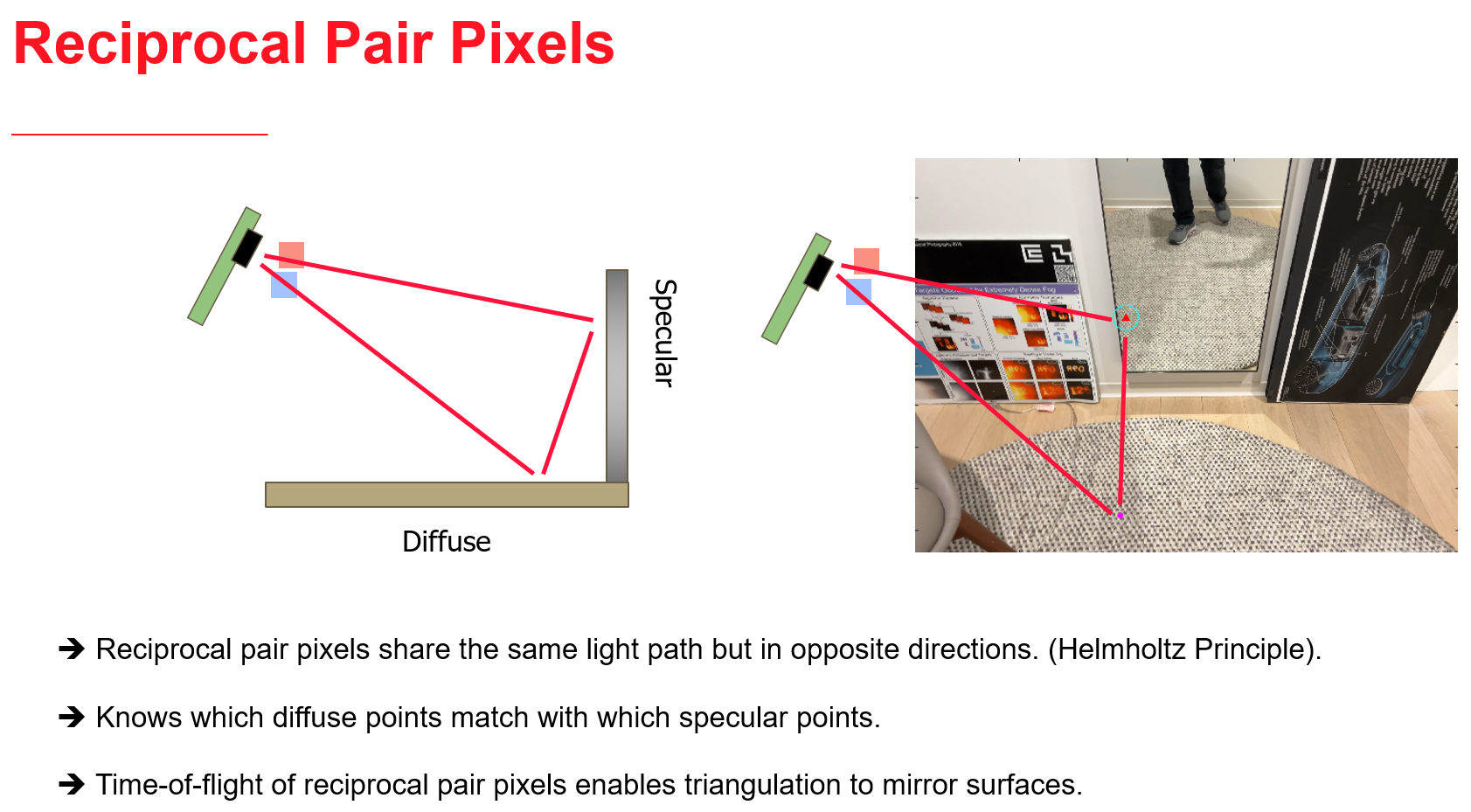
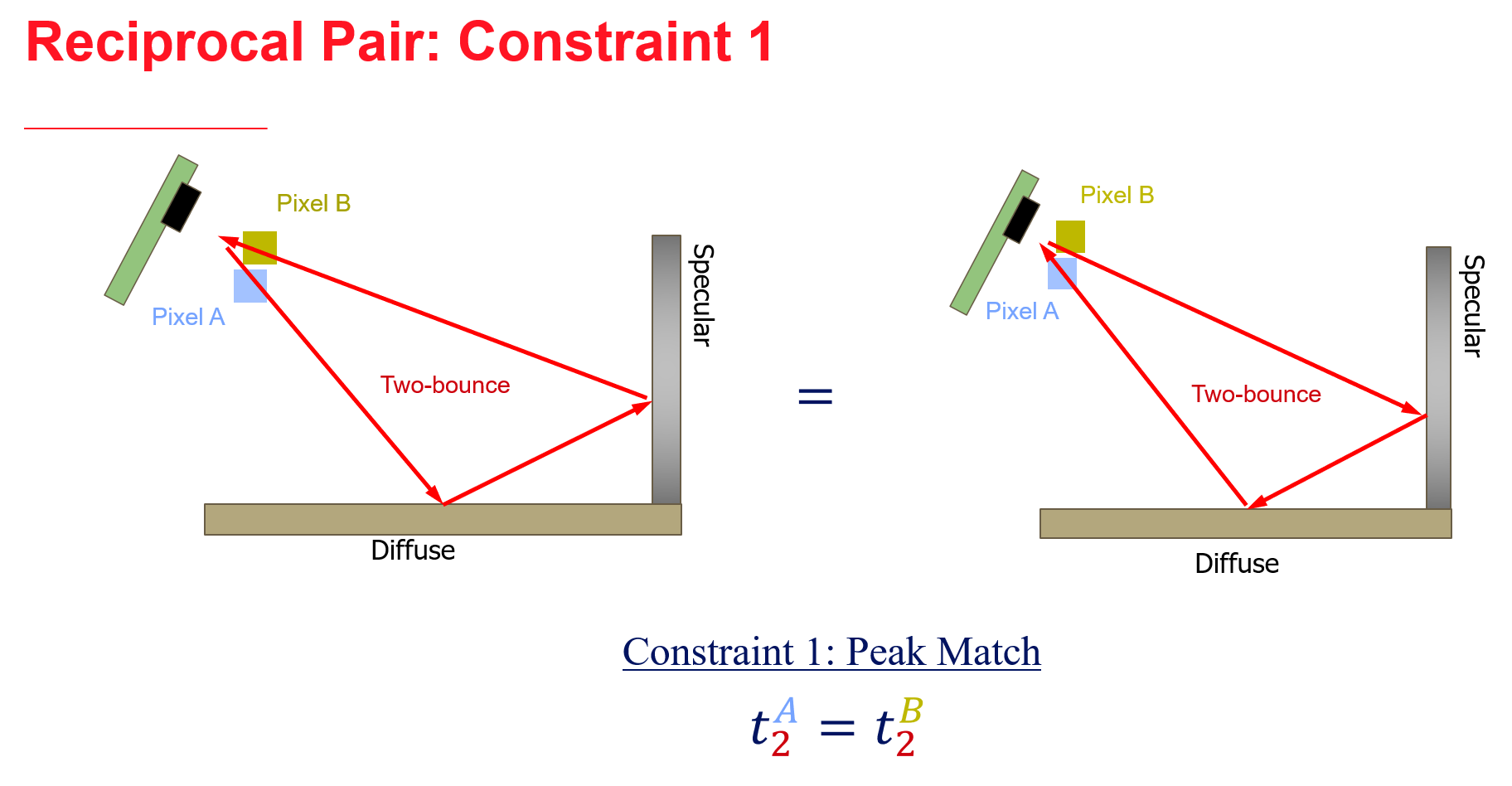
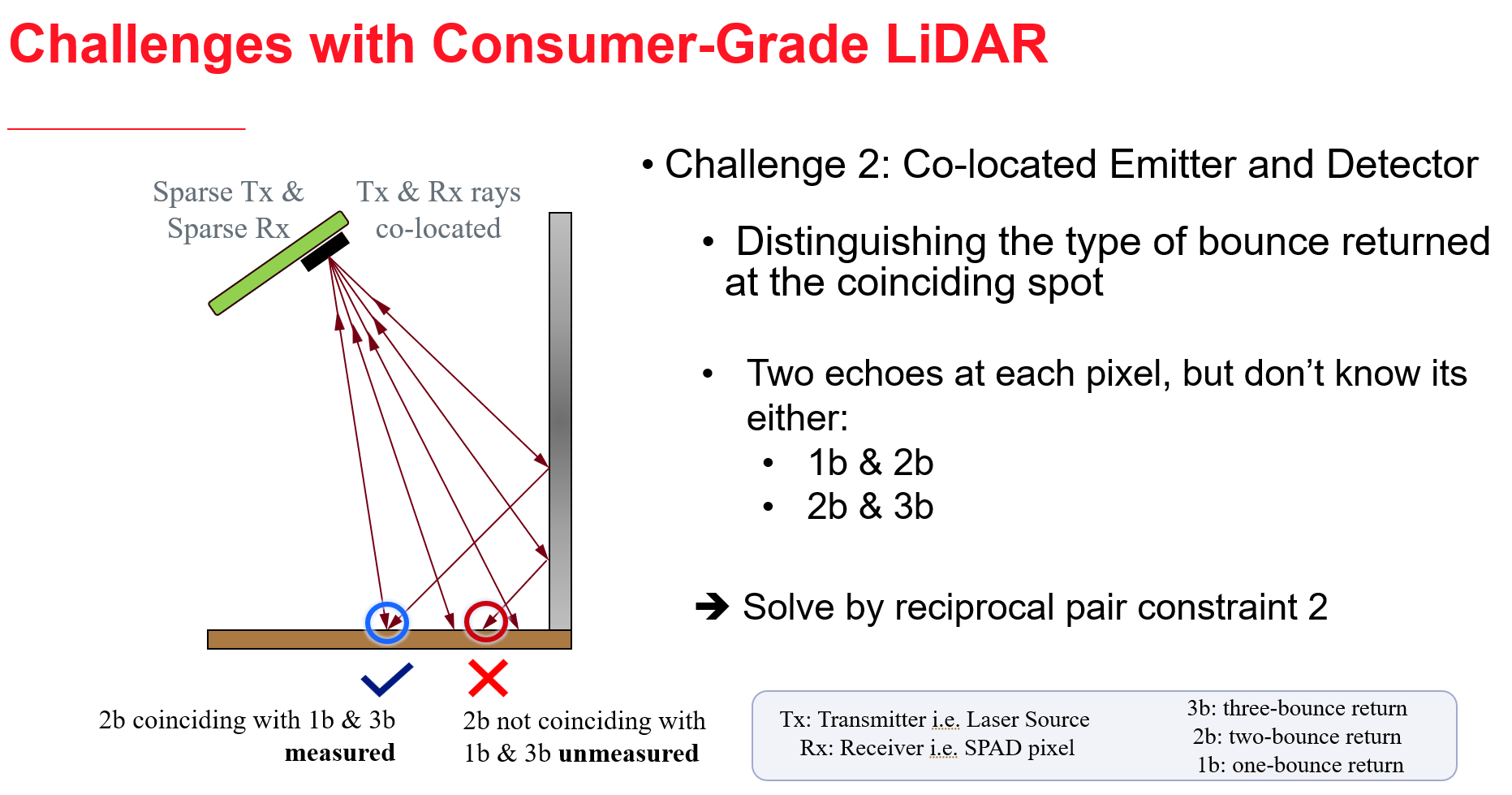
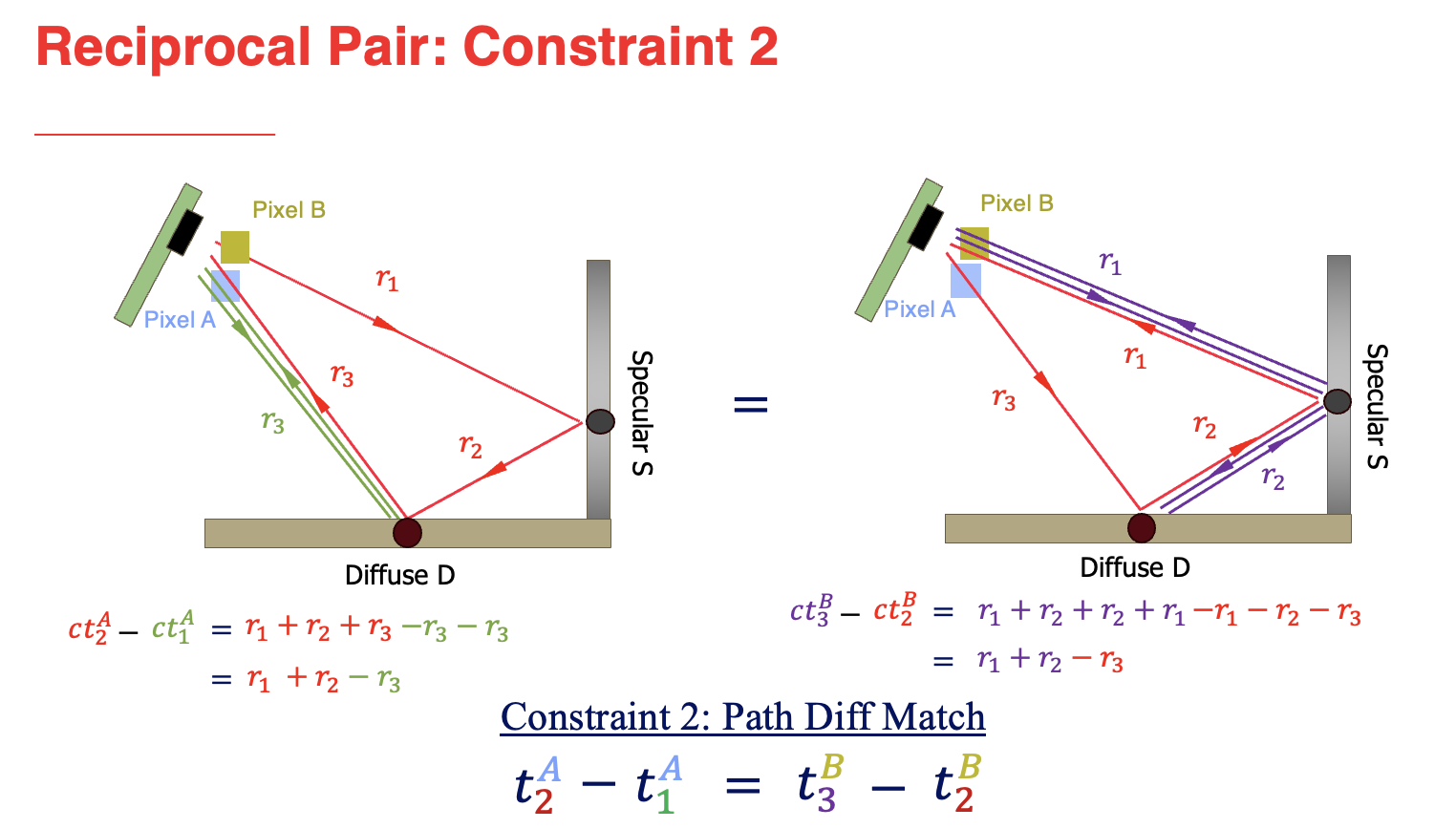
We propose an approach to leverage multi-bounce returns of a flash LiDAR on portable smartphones for 3D specular surface reconstruction. Traditional LiDAR systems assume that all returns are one-bounce returns, which can lead to an overestimation of the true mirror surface and cause it to appear as if there is a hole. However, in reality, returns from mirror surfaces follow multi-bounce paths. We operate with a consumer-grade, coarse multi-beam flash LiDAR, enabling real-time mapping on an affordable and portable smartphone. To address the challenges posed by the coarse setup, where the transmitter and receiver are co-located, we propose solving the association problem using the ’reciprocal pair’ algorithm. This algorithm can distinguish between different types of bounces from multi-bounce returns. We have demonstrated detection over multiple consecutive frames for dense mirror mapping. In addition to 3D reconstruction, we show that multi-bounce returns enhance performance in applications such as segmentation and novel view synthesis. Our method can be integrated with state-of-the-art learned-based models, enhancing their robustness in discerning ambiguous scenarios. Importantly, our approach can map various specular surfaces like mirrors and glasses without assuming specific shapes, and it can operate on non-perpendicular specular-diffuse surface pairs.








@inproceedings{lin2024lidarmirror,
title={Handheld Mapping of Specular Surfaces using Consumer-Grade Flash LiDAR},
author={Lin, Tsung-Han and Henley, Connor and Somasundaram, Siddharth and Dave, Akshat and Laifenfeld, Moshe and Raskar, Ramesh},
booktitle={2024 IEEE International Conference on Computational Photography (ICCP)},
year={2024},
organization={IEEE}
}